Fibonacci Prime | Write a program in Java to print the Fibonacci Primes | ICSE Computer Application | ISC Computer Science
Algorithm
- Start
- x:=0
- y:=0
- z:=0
- If x<=1, go to step 6 or else go to step 11
- Print "Enter the end point of the Fibbonacci Series"
- Read x
- If x<=1, go to step 9 or else go to step 10
- Print "Invalid Value. Try Again."
- Go to step 5
- y:=0
- z:=1
- If y<=x, go to step 14 or else go to step 28
- a=y
- count:=0
- If a>1, go to step 17 or else go to step 24
- i=2
- If i<a, go to step 19 or else go to step 22
- If a%i==0, go to step 20 or else go to step 21
- count++
- i++. Go to step 18
- If count==0, go to step 23 or else go to step 24
- Print y+", "
- sum=y+z
- y=z
- z=sum
- Go to step 13
- Stop
Program
Buffered Reader
import java.io.*;
class FibonacciPrimes
{
int x, y, z;
void accept() throws IOException
{
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
while (x<=1)
{
System.out.println("Enter the end point of the Fibonacci Series");
x=Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
if(x<=1)
{
System.out.println("Invalid Value. Try Again");
}
}
y=0;
z=1;
}
boolean isPrime(int a)
{
int count = 0;
if(a>1)
{
for(int i=2;i<a;i++)
{
if(a%i==0)
{
count++;
}
}
if(count==0)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
void display()
{
while(y<=x)
{
if(isPrime(y)==true)
{
System.out.print(y+", ");
}
int sum=y+z;
y=z;
z=sum;
}
}
void main() throws IOException
{
accept();
display();
}
}
Scanner
import java.util.*;
class FibonacciPrimes
{
int x, y, z;
void accept()
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
while (x<=1)
{
System.out.println("Enter the end point of the Fibonacci Series");
x=sc.nextInt();
if(x<=1)
{
System.out.println("Invalid Value. Try Again");
}
}
y=0;
z=1;
}
boolean isPrime(int a)
{
int count = 0;
if(a>1)
{
for(int i=2;i<a;i++)
{
if(a%i==0)
{
count++;
}
}
if(count==0)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
void display()
{
while(y<=x)
{
if(isPrime(y)==true)
{
System.out.print(y+", ");
}
int sum=y+z;
y=z;
z=sum;
}
}
void main()
{
accept();
display();
}
}
Documentation
Variable Description
| Data Type | Variable Name | Description |
| int | x | To store the end value of series |
| int | y | To store the value to be displayed |
| int | z | To store the previous value of the fibonacci series |
| int | sum | To store the sum of previous terms of series |
| int | count | To count the number of factors except one and itself |
| int | a | To parse a value to a method |
| int | i | To act as a counter variable |
Method Description
| Return Type | Method Name | Description |
| void | accept() | To accept data from the user |
| void | display() | To display the fibonacci primes |
| boolean | isPrime(int) | To check whether the argument is a prime number or not |
| void | main() | To call all the functions in the correct order |
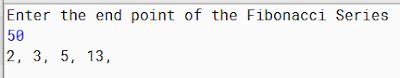
Output
Share with all ISC Computer Science Students you know.
Comment below with all your program requests and blog suggestions.
Follow us on social media by clicking on these links.
Instagram : @IscJavaCode
Twitter: @IscCode
Quora: ISC Java Code
Stay Healthy
Stay Happy
Stay Helpful







Comments
Post a Comment